Ingesting data from Kafka into Mach5
This document explains how to ingest data from Kafka topics into a Mach5 Search index by configuring connections, setting up ingest pipelines, and verifying ingestion using the Mach5 UI.
Prerequisites
- This document assumes that Mach5 is deployed and running successfully. Mach5 Administrative UI page looks as below. Lets assume it’s running at http://localhost:8888/

- Store, store route and warehouse are created successfully. Refer to Quickstart document for help
- Consider there is a Kafka topic named kafkatopic already set up having following 10 records:
@kafka-client$ kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.kafka.svc.cluster.local:9092 --topic kafkatopic --from-beginning
{ "id": "1", "ip_address": "192.168.1.1" }
{ "id": "2", "ip_address": ["192.168.1.2", "10.0.0.5"] }
{ "id": "3", "ip_address": "10.0.0.1" }
{ "id": "4", "ip_address": ["10.0.0.2", "8.8.8.8"] }
{ "id": "5", "ip_address": "172.16.0.1" }
{ "id": "6", "ip_address": ["172.16.0.2", "192.168.1.1"] }
{ "id": "7", "ip_address": "8.8.8.8" }
{ "id": "8", "ip_address": ["8.8.4.4", "10.0.0.5"] }
{ "id": "9", "ip_address": "192.168.2.1" }
{ "id": "10", "ip_address": ["192.168.2.2", "8.8.4.4"] }
Processed a total of 10 messages
- Mach5 Index is already created with the name kafkaindex and with relevant mappings for the kafka topic. If no mappings are provided, Mach5 will dynamically infer the mapping when ingesting data. Please note that some data may not get ingested if mappings are not provided.
Connections
Connection is the resource or the entity which stores the properties needed to connect or access the source where the data resides, for instance in Iceberg, Kafka or S3. It is important to note that the same connection can be used in multiple ingest pipelines
Click on Connections on the left panel of Mach5 UI
Add a new connection
Click on + icon on Connections page to create a new connection
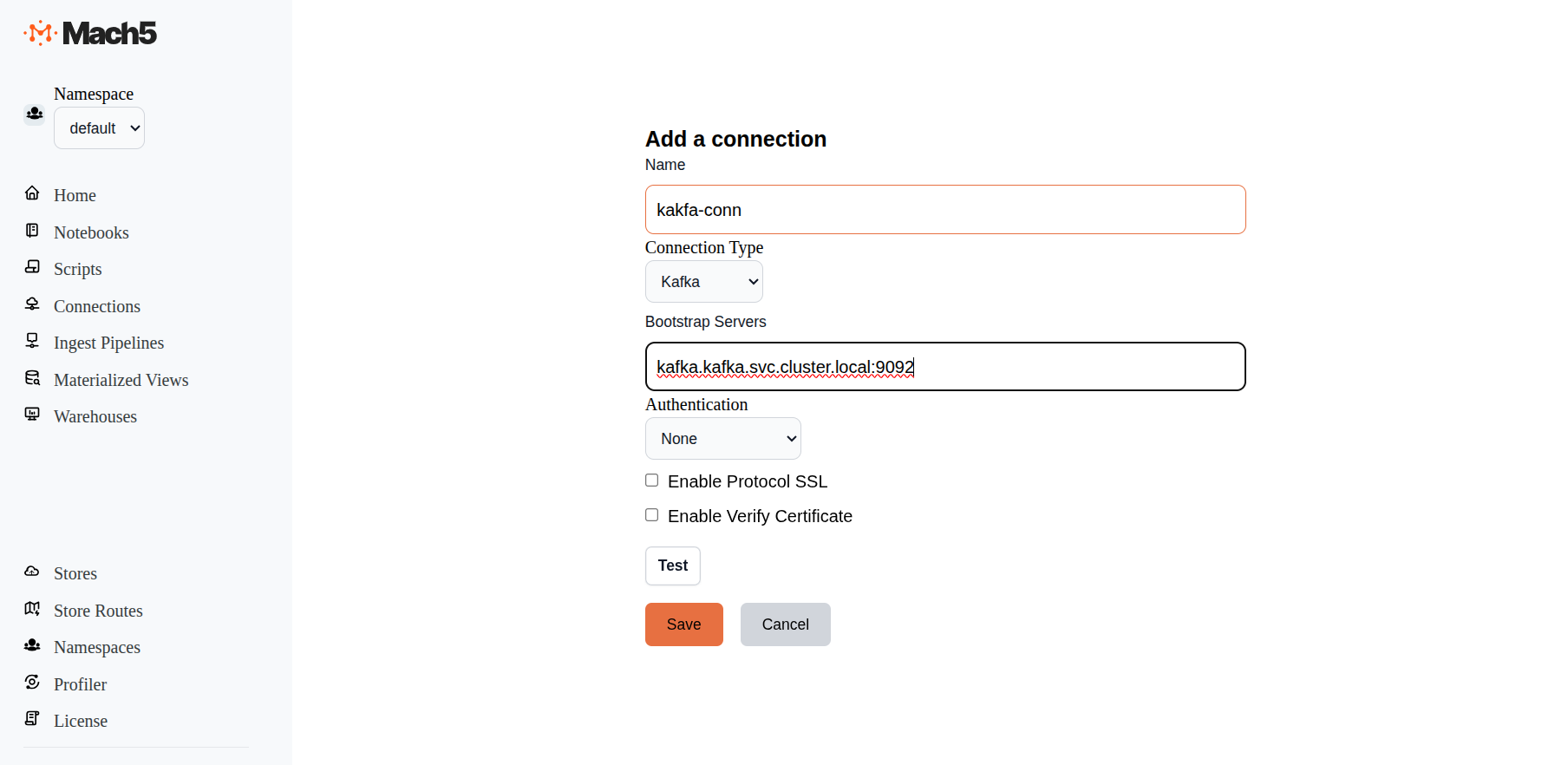
- Name: Provide a name for the connection, eg. kafka-conn
- ConnectionType: There are 3 options in dropdown: AwsS3, Iceberg, Kafka. Choose Kafka
- Bootstrap Servers: Specify the bootstrap server details. Eg: kafka.kafka.svc.cluster.local:9092
- Authentication: Keep it as default - None. Other option is AWS_MSK_IAM
- Enable Protocol SSL: Leave it deselected to use Kafka without SSL
- Enable Verify Certificate: Leave it deselected
- Test: Click on the Test button to verify connectivity to Kafka
- Click on Save
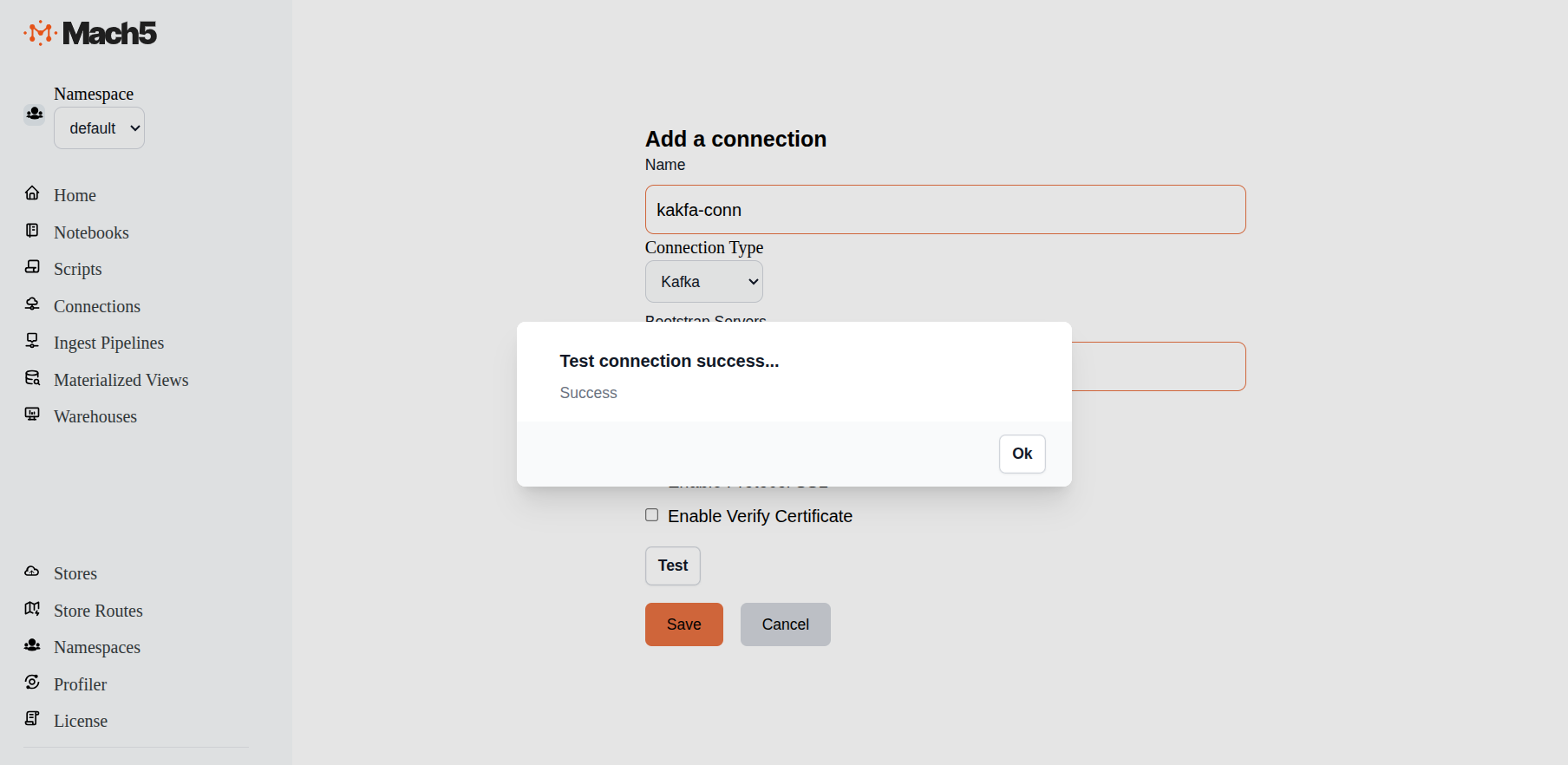
Verify new connection
Verify that the new connection is created in the Connections page

Ingest Pipelines
Mach5 Search ingest pipelines allow you to process and ingest documents from various different sources like Iceberg, Kafka. S3 bucket, etc. This is useful for transforming, enriching, or modifying data at ingestion time. To access the source data, ingest pipeline needs the specific connection to source data. For example if we are creating an ingest pipeline to index data from Kafka topic as data source, then you need a connection of type Kafka
Click on Ingest Pipelines on the left panel of Mach5 UI
Add an ingest pipeline
Click on + icon on Ingest Pipelines page to create a new ingest pipeline
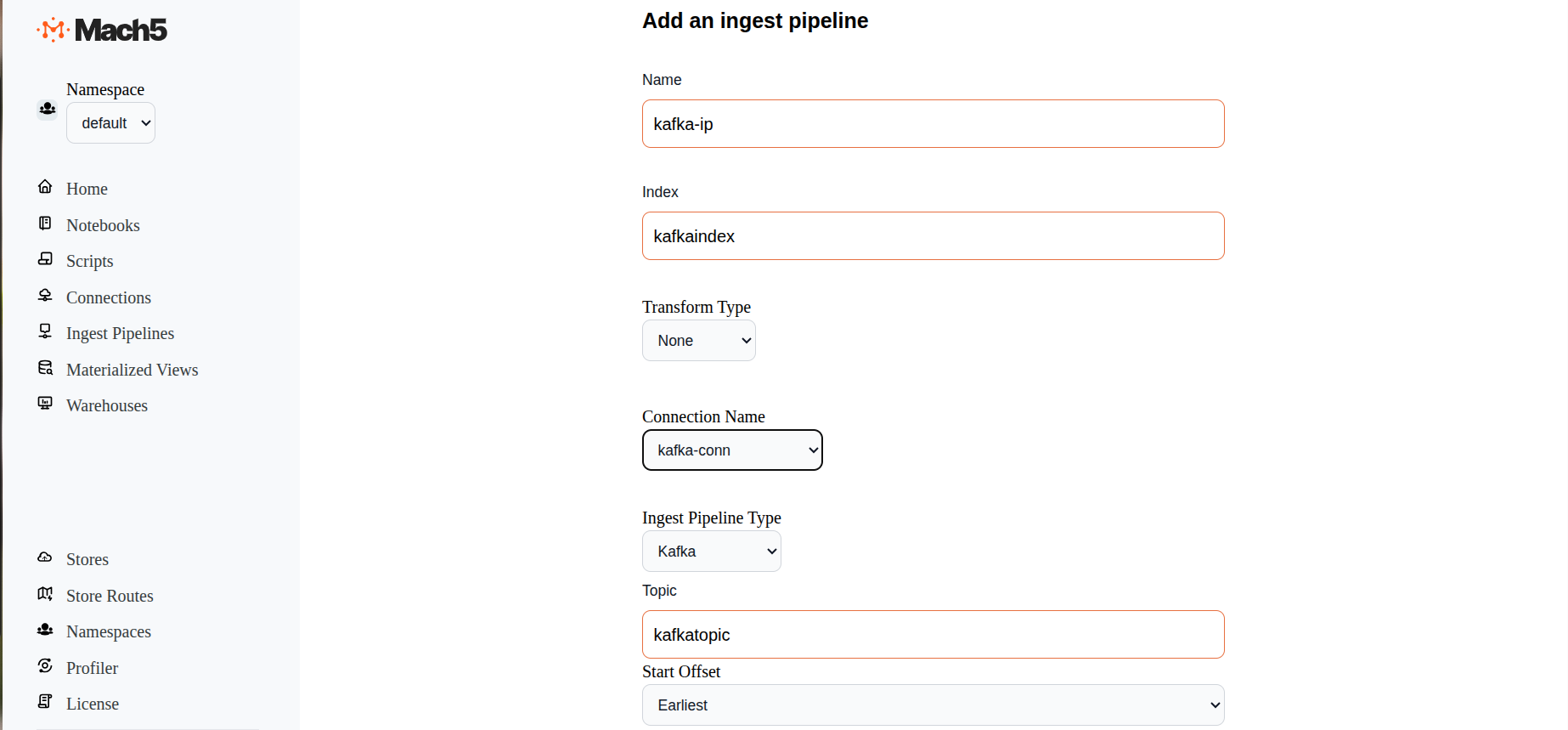
- Name: Provide name of the ingest pipeline, eg. kafka-ip
- Index: Specify name of the Mach5 index eg. kafkaindex. Please note that the index must be created in Mach5 prior to configuring the ingest pipeline
- Transform Type: Select options between None or Javascript. This helps to transform data before ingestion. If Javascript is selected, specify the script details in the given box
- Connection Name: Select the Kafka connection name that was created earlier
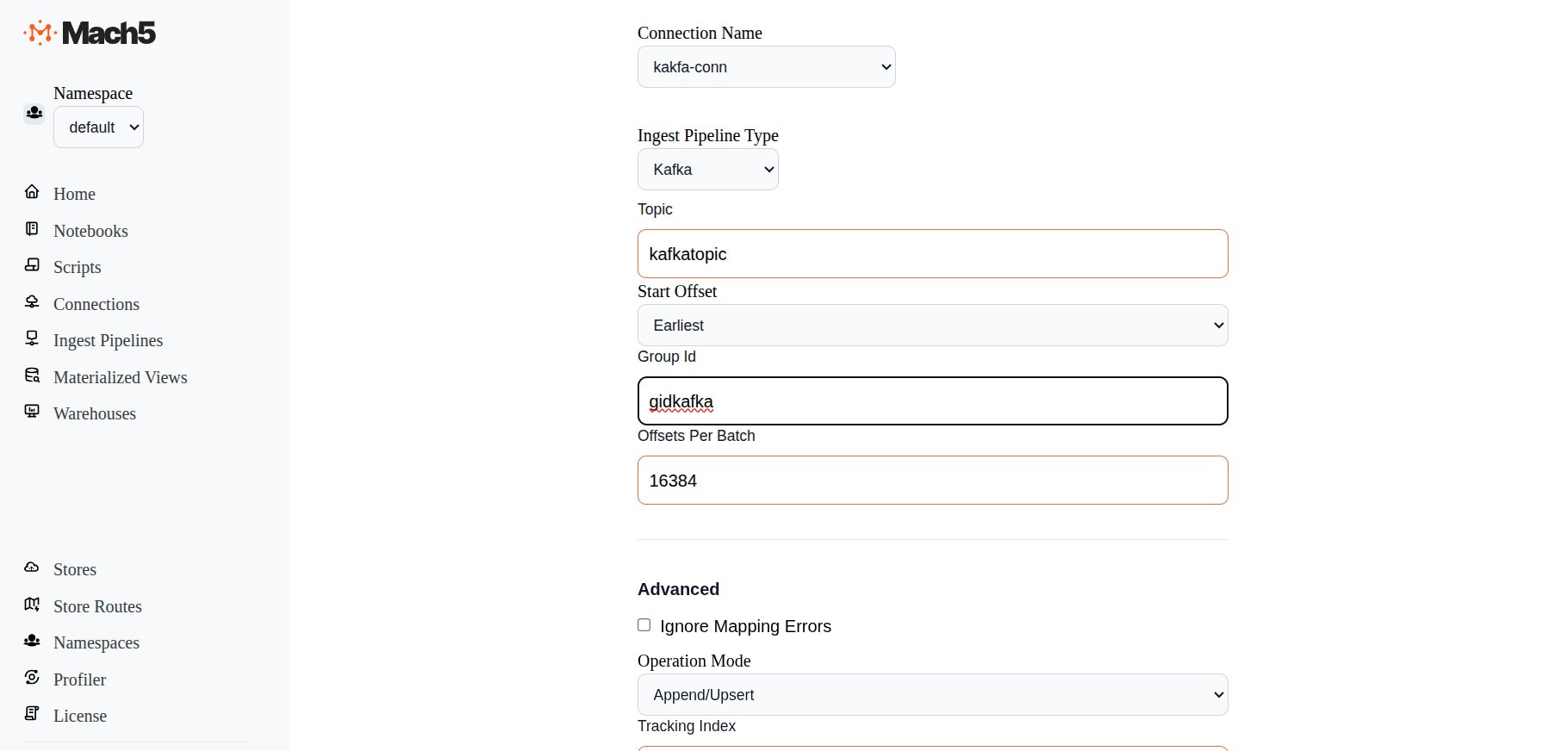
- Ingest Pipeline Type: Options are S3, Iceberg, Kafka. Select Kafka
- Topic: Specify the Kafka topic from which data needs to be ingested. Eg. kafkatopic
- Start Offset: Options are Earliest, Latest. Keep default as Earliest. Earliest means from the beginning of the topic. Latest means whatever data comes in the topic after the pipeline is setup
- Group Id: Specify the group Id, eg. gidkafka. The group id is the unique identifier for a Kafka consumer group
- Offsets Per Batch: Default is 16384. Specify the offset as needed, otherwise keep as default
- Advanced: Leave the advanced section as default, Operation Mode being Append/Upsert
- Enabled: Select this checkbox to Enable the Ingest Pipeline
- Click on Save
- Once the ingest pipeline is created, records will start getting reflected in the Mach5 index corresponding to the Kafka topic.
Verify an ingest pipeline
In Ingest Pipelines page verify if the ingestion pipeline is created properly

Once the kafka-ip ingestion pipeline is successfully created, records from Kafka in kafkatopic are ingested into Mach5 index kafkaindex. As and when new data comes to the Kafka topic, it will get added into the Mach5 index
Verify data ingestion
Using Mach5 Dashboards - Dev Tools verify that the data from Kafka is ingested into Mach5
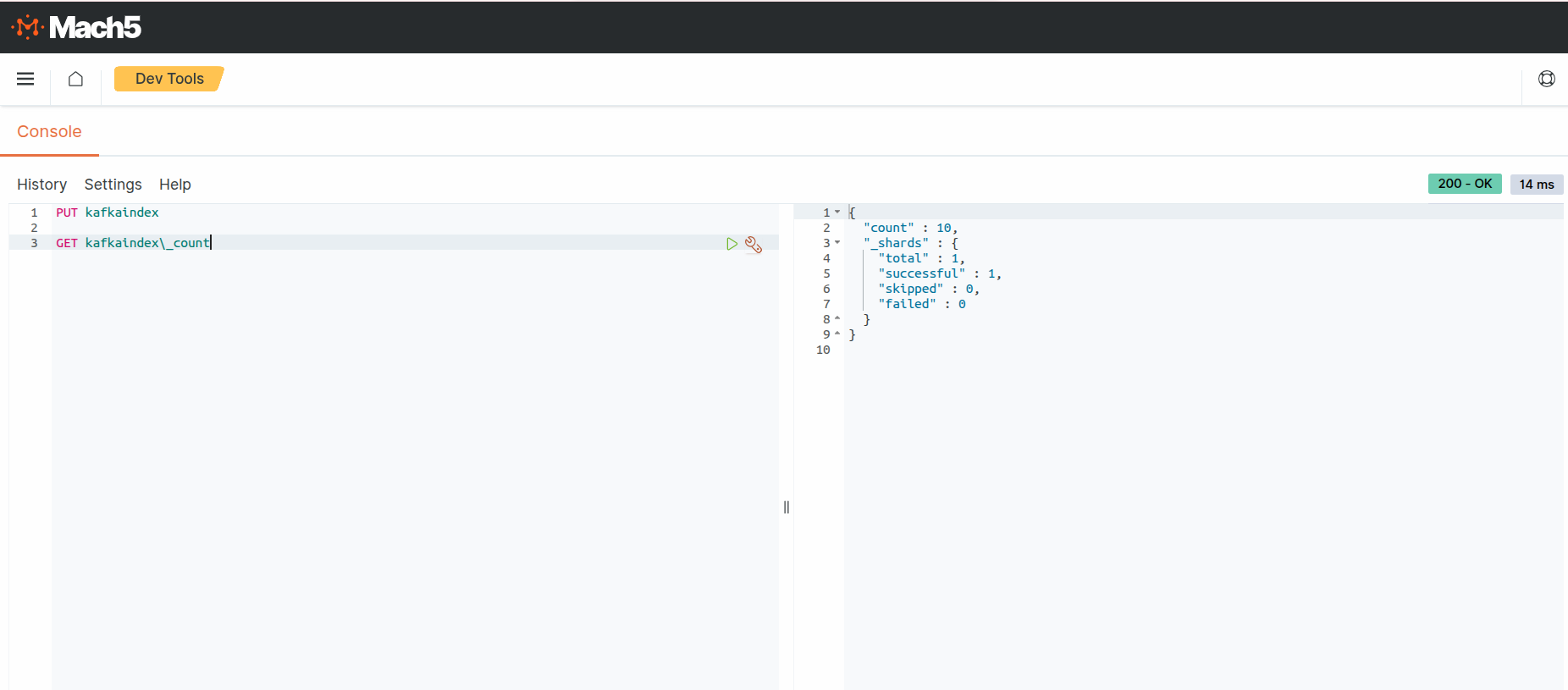
- Execute a count query on the Mach5 index to verify the number of ingested records. As expected, the count is 10 records. This is what was ingested into kafkatopic, refer to Prerequisites
- Execute a search query on the Mach5 index to verify the ingested records.
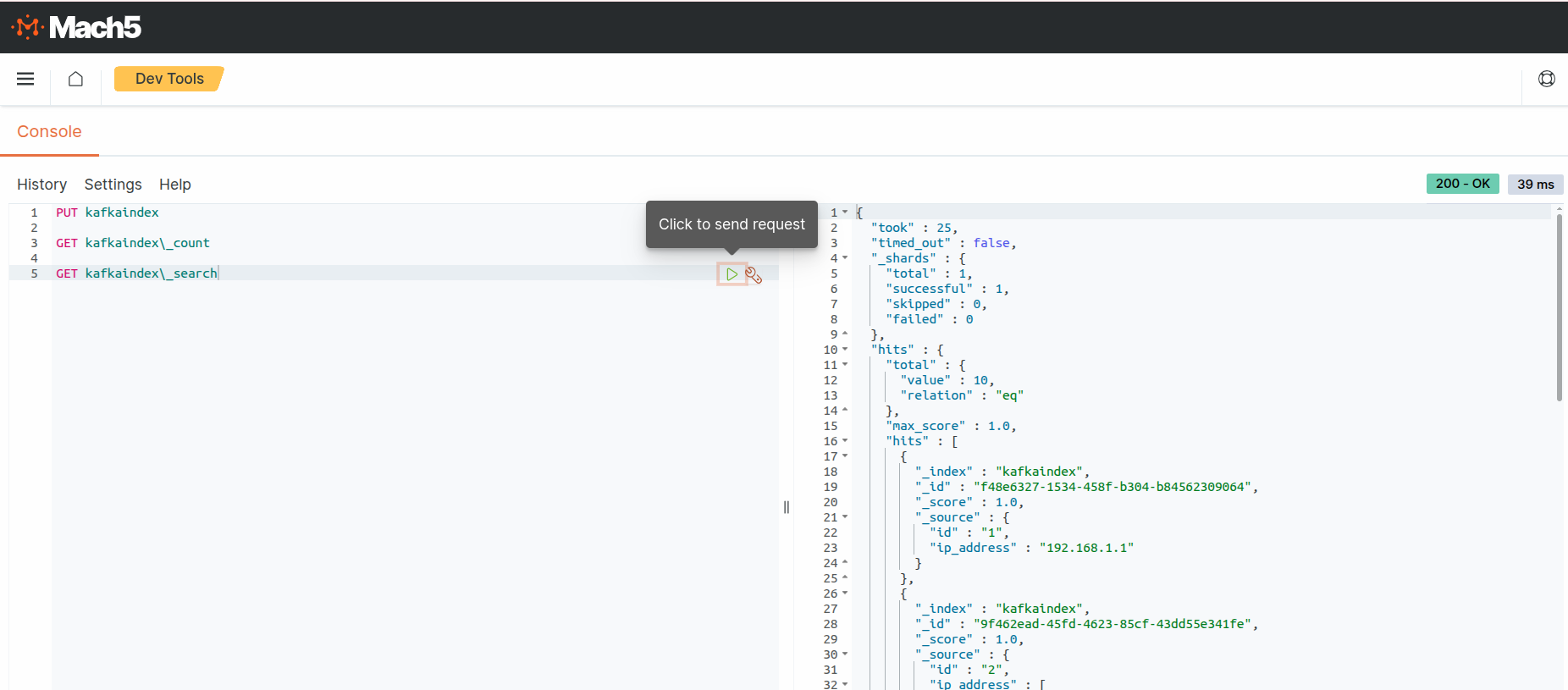
As expected, the output shows 10 ipdata records. This is what was ingested into kafkatopic, refer to Prerequisites
Disable ingest pipeline
When not in use, ingest pipeline can be disabled. So any updates to source data are not reflected in Mach5
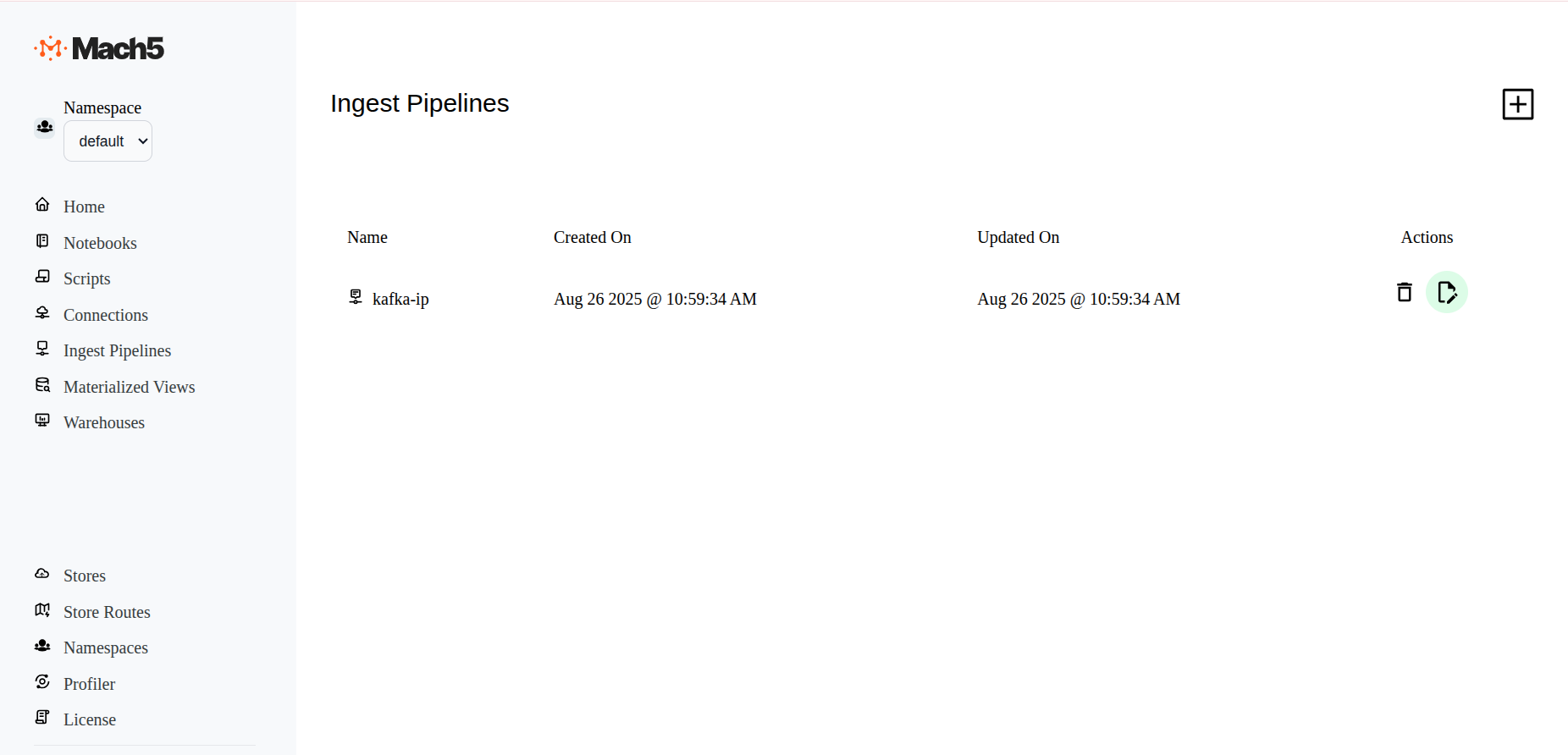
- To Disable an existing pipeline, click on the Edit icon next to the the ingest pipeline, eg. kafka-ip
- In the Edit ingest pipeline page, at end of all options, before Save button, deselect the Enabled checkbox
- Save the ingest pipeline to take effect
- The kafka-ip ingest pipeline is now disabled. It will not read data from source to ingest data into Mach5. It can be enabled any time it needs to be re-used
Kafka Tombstone Support in Mach5
Tombstone Messages
In Kafka, tombstone messages are messages with a valid, non-empty key and an empty/null payload (no value). Tombstone messages can be added to a topic by any producer and are often used in conjunction with compacted topics in order to delete previous instances of a particular key.
Transform functions are optional in Mach5 ingest pipelines. However, when ingesting Kafka tombstone messages, a transform function is required to explicitly define the desired tombstone handling behavior. When Mach5 detects a tombstone message, the meta.kafka.op field is set to "delete" for the record in the ingest pipeline. This field can be interpreted by the transform function in order to produce one of two outcomes:
- Delete: When the transform function returns a record containing a single
_idfield, the corresponding document in the index with the matching_idfield (if it exists) will be deleted. Including any fields other than_idwill result in an error. - Ignore: When the transform function returns the empty array
[], no action will be performed on the index.
Examples
Deleting with Tombstone Messages
The following transform function shows how to (explicitly) interpret and act upon a delete operation.
Note: The following example assumes that the Kafka record key is non-null and UTF-8–encoded, and that it maps directly to the document _id. This is a common pattern, but not a requirement. Applications with different key encodings or error-handling needs should decode and validate the key accordingly (for example, using try/catch).
function transform(payload, meta) {
const kafka = meta?.kafka;
// Assumes the key is not null and is a valid UTF8 string
const id = decodeUtf8(new Uint8Array(kafka.key));
if (kafka?.op === "delete") {
return { _id: id };
} else {
// Further processing and transformation of payload
return { ...payload, _id: id};
}
}
const rec = transform(arg, meta);
rec
A more compact version of this function can be written to take advantage of JavaScript object spreading semantics:
function transform(payload, meta) {
const kafka = meta?.kafka;
const id = decodeUtf8(new Uint8Array(kafka.key));
return { ...payload, _id: id };
}
const rec = transform(arg, meta);
rec
When the operation is a delete, arg/payload is null, so spreading is a no-op in JavaScript, producing a single object with the _id field as required.
Ignoring Tombstone Messages
The following example shows how to explicitly ignore tombstone messages while continuing to process non-tombstone records:
function transform(payload, meta) {
const kafka = meta?.kafka;
if (kafka?.op === "delete") {
return [];
}
// Normal processing for non-tombstone records
return payload;
}
Troubleshooting
Issue: Ingest pipeline does not work and no new pods are being spawned
- Symptom: The ingest pipeline appears to be configured but no data is ingested.
- Cause: The Mach5 index referenced in the ingest pipeline does not exist.
- Resolution: Ensure that the required Mach5 index is created before configuring or enabling the ingest pipeline.